 Electrical components including PCBs, wires, and other assemblies require a form of “seal” to protect them from environmental exposures that could result in electrical shorts, sparks or complete electrical failure.
Electrical components including PCBs, wires, and other assemblies require a form of “seal” to protect them from environmental exposures that could result in electrical shorts, sparks or complete electrical failure.
There are a variety of products and techniques on the market used to create these seals. For today’s discussion we will focus on the product Hysol® US4028. Hysol® is a product line of Henkel.
Hysol® US4028 is a flexible polyurethane elastomer formulated for general potting and encapsulation, particularly used for electrical components.
 Potting is the technique used to surround, coat or envelop an electronic component in a liquid resin to protect it from environmental conditions.
Potting is the technique used to surround, coat or envelop an electronic component in a liquid resin to protect it from environmental conditions.
Similarly, encapsulation is the technique in which an electrical component is surrounded, coated or enveloped in a solid resin to protect it from environmental conditions.
The compounds used in Hysol® US4028 provide mechanical reinforcement to housed assemblies, fill large voids, and protect components from exposure to chemicals, moisture, mechanical shock and vibration.
Its many positive properties include low viscosity, low moisture resistivity, and excellent tear and abrasion resistance.
When working with this product it is important to note the respiratory hazards present and implement adequate engineering safety controls.
A + B = Hazardous Fumes
Hysol® US4028 is made up of two polyurethane components, Part A – Resin and Part B – Hardener. Each component must be pre-mixed before they are mixed together. The mixed ratio by volume is 5.4 : 1.0 (Part A : Part B).
|
Part A Hazardous Components & Exposure Limits |
|
| Polyurethane Resin | No established exposure limits |
| Dicyclohexylmethane-4 | NIOSH REL: 0.01 ppm (0.11 mg/m3)ACGIH TLV: 0.005 ppm TWA |
|
Part B Hazardous Components & Exposure Limits |
|
| Butyl benzyl phthalate | No established exposure limits |
| m-Phenylenediamine | ACGIH TLV: 0.1 mg/m3 TWA |
| N-Methyl-2- pyrrolidone | AIHA WEEL: 10 ppm TWA |

Once both parts are combined, the mixture must cure. Cure conditions depend on time and temperature. The below cure schedule is from the product’s technical data sheet.
|
Typical Curing Schedule |
||
|
Time |
Temperature |
Notes |
| 21 hours | 77° F | Plus 2.4 hours at 165° F – 185° F |
| 16 hours | 156° F – 163° F | |
| 8 hours | 165° F – 185° F | |
| 7 days | 77° F | For full properties |
 Most of these cure times require an elevated temperature which means a heating element must be used.
Most of these cure times require an elevated temperature which means a heating element must be used.
When heated, the mixture can form into vapor which then emits volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the air.
The material safety data sheets (MSDS) for both Part A and B contain numerous cautions about inhaling these compounds. Here is a snapshot of the cautions listed.
Part A
- Harmful if inhaled
- May cause respiratory tract irritation
- May cause lung damage
- Inhalation of dicyclohexylmethane-4 at concentrations above the TLV can irritate the mucous membranes causing sore throat, cough, chest discomfort, shortness of breath and reduced lung function.
Part B
- May cause respiratory tract irritation
- Butyl benzyl phthalate exposure may effect the central nervous system, pancreas, liver and kidney
- m-Phenylenediamine exposure may effect the bladder, liver, kidney and central nervous system
- N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidinone exposure may effect the bone marrow, central nervous system, immune system and lungs
As you can see, it is important to protect the respiratory zone of workers who may be exposed to these compounds during the mixing and curing process.
Contained workspace, chemical filtration
In addition to the health hazards listed in the MSDS, both documents recommend a form of local ventilation to keep the airborne concentration of these compounds at or below their established exposure limit.
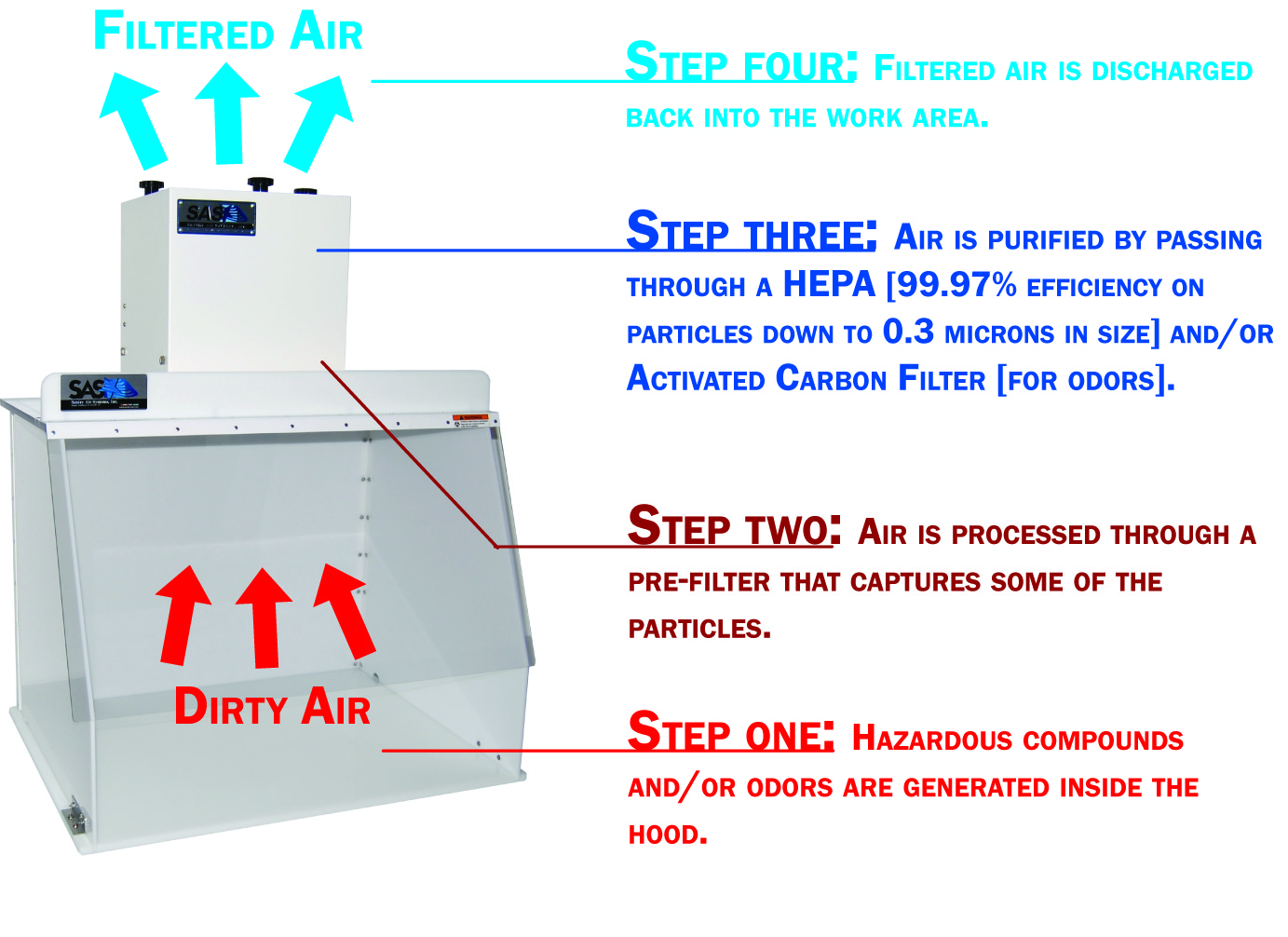
We recommend a ductless containment hood with an activated carbon filter for the capture and filtration of these hazardous compounds.
A ductless containment hood creates a semi-enclosed, negative pressure work environment where contaminated particles are arrested at the source of emission.
These particles are pulled into the filter chamber where the activated carbon filter adsorbs the particles before recirculating filtered air back into the surrounding area.
By going ductless, the hood is portable and can easily move around a workspace, so you aren’t locked into an exterior exhaust port.
Our ductless fume hoods come in a variety of sizes and airflow and can be customized to suit your unique application.
Sentry Air Systems demonstrates how our activated carbon filters work – YouTube Video

 Made in the USA
Made in the USA