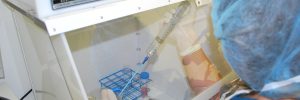
Introducing Portable Clean Rooms – Generation II (PCR2). This system features an updated design that provides the operator with easy fan control, improved airflow, and efficiency. This line also offers larger sizes with the same dependability. Portable Clean Rooms – Generation II Updated Features Clean and Sleek Look The Portable Clean Room Generation II offers… Learn More

 Made in the USA
Made in the USA